High-speed milling generally uses high milling speeds, proper feed rates, and small radial and axial milling depths. In general, the milling speed of high-speed milling is 5 to 10 times higher than the conventional speed, and the material removal rate is more than 3 to 5 times that of conventional milling. When milling, a large amount of milling heat is carried away by the chips, so the surface temperature of the workpiece is low [2]. As the milling speed increases, the milling force decreases slightly, the surface quality increases, and the machining productivity increases. However, in the high-speed machining range, the increase in milling speed will increase the wear of the tool, as shown in Figure 1.
Natural Graphite , as its name implies, is naturally formed by natural Graphite , which is generally found in graphite schist, graphite-gneiss, graphite-bearing schist and metamorphic shale.
Features
The chemical composition of graphite is carbon (C). Naturally produced graphite is rarely pure and often contains impurities, including SiO2, Al2O3, MgO, CaO, P2O5, CuO, V2O5, H2O, S, FeO and H, N, CO2, CH4, NH3, etc. Natural graphite minerals are black, steel gray, striated black; Metallic luster, crypto, dull, opaque; The hardness is isotropic, the vertical cleavage surface is 3 ~ 5, the parallel cleavage surface is 1 ~ 2; Qualitative soft, density is 2.09 ~ 2.23 g/cm3, have the feeling of greasy, easy to contaminate finger. Mineral chip under the transmitted light is generally not transparent, extremely thin can pervious to light, the light green gray, refractive index of 1.93 ~ 2.07, under the reflected light is light gray, reflective pleochroism, Ro gray with brown, Re dark blue gray, reflectivity Ro23 (red), Re5.5 (red), the reflected color, double reflection were significantly, strong heterogeneity, polarization color for straw yellow.
Graphite is a complex six-party double cone, assumes the six-party tabular crystal, common simplex are parallel double, six-party double cone, hexagonal prism, but in good condition with rare crystal forms, the generally show scaly or platy, aggregate density lump, earthy or globular.
Type
The process performance and usage of graphite is mainly depends on the degree of crystallization, in accordance with its natural Graphite Crystal morphology can be divided into crystalline graphite, Flake Graphite ) and aphanitic graphite (earthy graphite) two types of industry.
Crystalline graphite
In the crystalline (scale) graphite ore, the diameter of graphite crystals is greater than 1 mu m. Ore grade is low, but optional; The mineral associated with graphite is usually mica, feldspar, quartz, diopathic stone, diabase, garnet and a small amount of pyrite, calcite, etc., some of which have some useful components, such as rutile and vanadium. The ore is scales, grainy scales or granulocyte structures, flaky, flaky, or blocky structures.
Crystalline (scale) graphite is divided into High Purity Graphite, High Carbon Graphite, Medium Carbon Graphite and low Carbon Graphite according to the fixed carbon content.
The high purity graphite (fixed carbon content is greater than or equal to 99.9%) is mainly used for flexible graphite sealing material, nuclear graphite, instead of platinum crucible for chemical reagent melting and lubricant base material, etc.
High carbon graphite (fixed carbon content 94.0% ~ 99.9%) is mainly used for refractory materials, lubricant substrate, brush raw materials, carbon products, battery raw materials, pencil materials, filling materials and coatings, etc.
Carbon graphite (80% ~ 94% fixed carbon content) is mainly used for crucible, refractories, casting materials, foundry coatings, pencil raw materials, battery materials and dyes, etc.
Low carbon graphite (fixed carbon content 50.0% ~ 80.0%) is mainly used for foundry coatings.
Cryptocrystalline graphite
Cryptocrystalline graphite is also called soil graphite or amorphous graphite. In cryptocrystalline graphite ore, graphite crystals are less than 1 mu m in diameter, which are microcrystalline and can only be seen in the electron microscope. High grade of ore, but poor selectable; The mineral associated with graphite is often quartz and calcite; The ore is microscaly - cryptocrystalline structure, block or soil structure.
Cryptocrystalline graphite ore is mainly distributed in contact metamorphic deposits. Actually the diameter graphite flake graphite ore is uneven, the so-called crystalline graphite ore, may also contain the aphanitic graphite, are too many content is often referred to as the mixed type graphite ore, may also contain a small amount of aphanitic graphite quality mineral crystalline flake graphite piece diameter slightly larger than 1 microns.
Cryptocrystalline graphite ore is mainly used in pencil, battery, electrode, graphite emulsion, graphite bearing ingredients and the raw materials of battery carbon rod. The non-ferrous graphite is mainly used for casting materials, refractory materials, dyes and electrode paste.
Natural Graphite Natural Graphite,Expanded Graphite,Colloidal Graphite,Special Graphite Fengcheng Ruixing Carbon Products Co., Ltd , http://www.lnfcrxts.com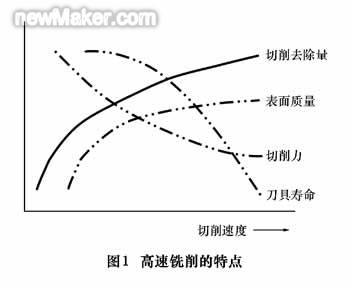
High-speed cutting has special process requirements than traditional cutting. In addition to high-speed cutting machines and high-speed cutting tools, it is also crucial to have the right CAM programming software. An excellent high-speed machining CAM programming system should have high calculation speed, strong interpolation function, full automatic cut inspection and processing capability, automatic tool holder and fixture interference check, feed rate optimization processing function, tool path editing Optimization function, processing residual analysis function, etc. The software that is mature at home and abroad for high-speed machining programming includes Unigraphics NX from Siemens, PowerMill from DelCAM in the UK, and Cimatron software from Israel. Among them, PowerMill of DelCAM in the UK has an outstanding advantage in 3D processing.
The NC code in high-speed cutting is not limited to different values ​​of cutting speed, depth of cut and feed. NC programmers must change all of their machining strategies to create effective, accurate, and safe toolpaths to achieve the desired surface accuracy [2]. In NC programming, we must first pay attention to the safety and effectiveness of the machining method. Secondly, we must do everything possible to ensure that the tool path is smooth and stable, which will directly affect the machining quality and the life of the machine tool spindle and other parts. Finally, we should try to make the tool load even, this will Directly affect the life of the tool. The specific requirements for high-speed cutting for NC programming are as follows.
1. 1 maintain a constant cutting load
It is important to maintain a constant cutting load during high-speed milling, which directly affects the machining quality of the workpiece and the life of the machine spindle and tools.
1. 1. 1 keep the metal removal constant
Constant metal removal during processing results in better processing quality and extended tool and machine life due to uniform cutting loads. In order to maintain constant cutting conditions, roughing is mainly used for down milling. The use of down-milling in high-speed cutting can produce less cutting heat, reduce tool load, reduce or even eliminate work hardening of the workpiece, and obtain better surface quality. In the case of uneven workpiece allowance, a constant machining strategy is usually used to ensure a constant metal removal. The method used for roughing is usually to cut a continuous plane in the Z direction, also called a contour processing strategy. This cutting follows the theory of high speed machining and uses a smaller depth of cut than conventional cutting to reduce the amount of cutting per tooth. Figure 2 is a schematic diagram of the continuous plane of cutting in the Z direction. Usually this type of machining adopts oblique or spiral cutting to obtain a smoother cutting path. 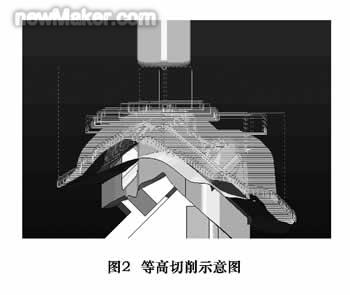
(6) Obtain better processing quality, etc. [1].
